2019年10月11日,国际著名病原学权威期刊PLOS Pathogens在线发表了武汉大学生命科学学院,病毒学国家重点实验室陈宇教授和中山大学医学院郭德银教授合作的最新成果,该研究揭示了P200家族蛋白对抗病毒天然免疫调控的新机制。原文题目为“P200 family protein IFI204 negatively regulates type I interferon responses by targeting IRF7 in nucleus”(P200家族蛋白IFI204通过IRF7负调控I型干扰素反应)。

干扰素介导的先天免疫反应对控制病毒感染有很重要的作用。它是通过宿主模式识别受体识别病原相关模式分子而开始的。例如,病毒RNA被RIG-I 样受体 (RLR) 和TOLL样受体 (TLR) 识别;病毒DNA被cGAS 和AIM2样受体 (ALR)识别等。这些受体能进一步激活下游IRF3和IRF7介导的I型干扰素的表达。ALR属于P200家族蛋白 (也称为PYHIN或HIN-200蛋白) 的成员。在以往的研究报道中,以AIM2、IFI16为代表的ALRs通过识别病毒DNA来激活下游I型干扰素的表达及炎症反应。在本研究中,作者通过蛋白质组和转录组联合分析,发现在DNA或RNA病毒感染小鼠骨髓来源树突状细胞(BMDCs)后,P200家族蛋白IFI204(IFI16的鼠同源蛋白)被激活,表达水平显著提高(图1)。
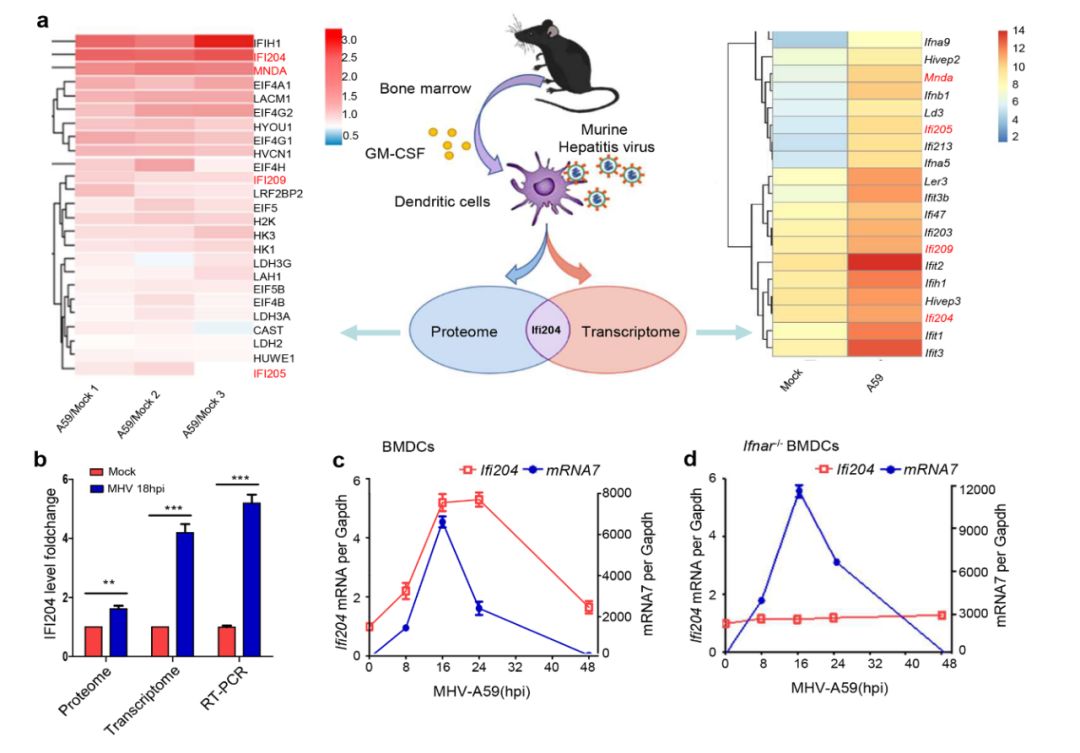
图1. 冠状病毒科鼠肝炎病毒(MHV)感染小鼠骨髓来源树突状细胞(BMDCs)后,包括IFI204在内的P200家族蛋白(例如IFI205,IFI209和MNDA)表达水平显著提高。
研究发现,尽管DNA病毒和RNA病毒感染均引起P200家族蛋白表达水平升高,但其调控I型干扰素反应的功能却截然不同。在RNA病毒感染的过程中,高表达的IFI204显著抑制了I型干扰素反应,揭示IFI204蛋白可能还具有负调控抗病毒天然免疫反应的作用。进一步研究发现,IFI204的HIN结构域能通过剂量依赖的方式结合干扰素调节因子7(IRF7)的DBD 结构域,阻止其与下游特异启动子的结合,从而抑制IRF7激活后介导的I型干扰素的转录,在RNA病毒感染后期防止天然免疫系统的过度活化(图2)。而DNA病毒感染主要激活IRF3介导的信号通路,且不能有效激活IRF7介导的信号通路,也观察不到IFI204的负调控功能。因此在DNA病毒感染早期,P200家族蛋白(例如AIM2、IFI16)主要通过识别病毒DNA,协同cGAS-STING激活I型干扰素反应。随后的研究发现,其他主要P200家族蛋白均具有结合IRF7从而负调控其介导的I型干扰素反应的功能(图2)。该研究揭示了P200家族蛋白通过IRF7负调控天然免疫通路的新功能,为研究病毒感染引起的天然免疫调控提供了新的视野。
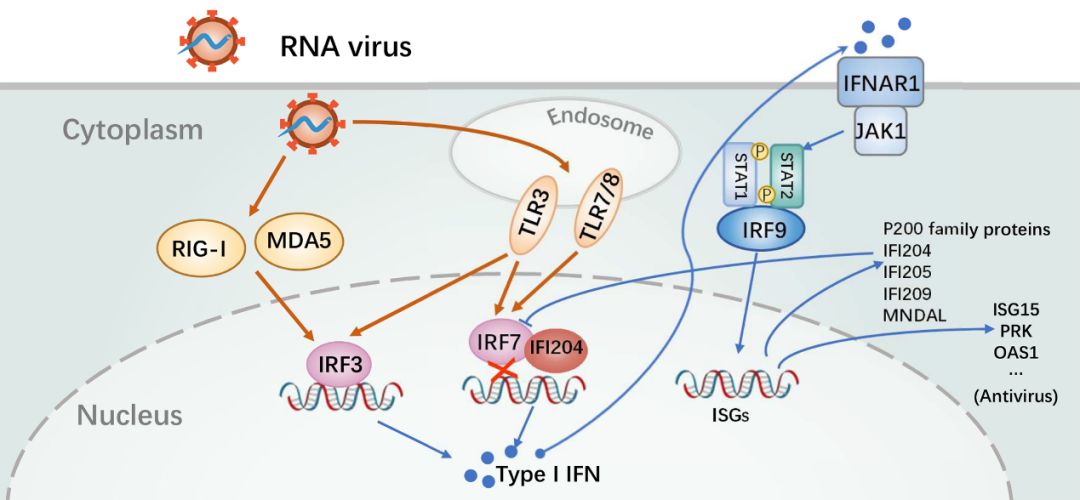
图2. P200家族蛋白负调控IRF7介导的I型干扰素反应示意图。RNA病毒感染后期,被诱导高表达的P200家族蛋白通过结合IRF7进而抑制其下游的基因转录。
武汉大学生命科学学院,病毒学国家重点实验室陈宇教授和中山大学医学院郭德银教授为本论文共同通讯作者,武汉大学生命科学学院赵晓璐副教授以及中山大学医学院的李春梅副教授为本论文合作者。武汉大学生命科学学院博士研究生曹流为第一作者,该生获得病毒学国家重点实验室吉凯奖学金资助。该项目获得国家科技重大专项(2018ZX10733403)、国家自然科学基金(81672008、81620108020)和湖北省自然科学基金(2018CFA035)的联合资助。
原文链接:
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1008079
Abstract
Interferon-inducible p200 family protein IFI204 was reported to be involved in DNA sensing, and subsequently induces the production of type I interferons and proinflammatory mediators. However, its function in the regulation of antiviral innate immune signaling pathway remains unclear. Here we reported a novel role of IFI204 that specifically inhibits the IRF7-mediated type I interferons response during viral infection. IFI204 and other p200 family proteins are highly expressed in mouse hepatitis coronavirus-infected bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. The abundant IFI204 could significantly interact with IRF7 in nucleus by its HIN domain and prevent the binding of IRF7 with its corresponding promoter. Moreover, other p200 family proteins that possess HIN domain could also inhibit the IRF7-mediated type I interferons. These results reveal that, besides the positive regulation function in type I interferon response at the early stage of DNA virus infection, the interferon-inducible p200 family proteins such as IFI204 could also negatively regulate the IRF7-mediated type I interferon response after RNA virus infection to avoid unnecessary host damage from hyper-inflammatory responses.
Author summary
The regulation of type I interferon signaling pathway is dynamic sequential processes and must be tightly regulated to keep balance between antiviral immune and hyper-inflammatory responses. The precise regulation mechanisms of the innate immune signaling pathway are still worth studying. Here, we found a novel role of the interferon-inducible p200 family protein IFI204 that specifically inhibits the IRF7-mediated type I interferon production by negative control of the transcriptional activity of IRF7 in the nucleus at the late stage of RNA virus infection. Previous studies showed that IFI204 is involved in DNA sensing during DNA virus infection to initiate antiviral immune responses. We demonstrate that IFI204 can inhibit IRF7-mediated activation of type I IFN responses induced by RNA virus infection, which is in contrast with its role in IRF3 activation in cGAS-STING DNA sensing pathway during DNA virus infection. Such negative regulation may help to avoid hyper-inflammatory responses induced by the over-activated IRF7-mediated type I interferons at late stage of the viral infection. Thus, the current study sheds light on the regulation roles of p200 family proteins and the accurate regulation system of type I interferons signaling pathway.来源:中国病毒学英文版
本期编辑:Tony

